
AutoSys is used for defining, scheduling and monitoring jobs. These jobs can be a UNIX script, java program or any other program which can be invoked from shell. Before starting we assume that user has already setup an AutoSys environment. This environment consists of autosys server and autosys client.
They can also be commsnds to set a global variable or to cancel the scheduled event. An AutoSys job is any single command, executable, script, or Windows batch file. AutoSys Commands List with Examples – Cheat Sheet. To list the Forecast report of the jobs running at particular time interval: In case of dual servers it checks both the databases. AutoSys Frequently Use Commands. To run AutoSys jobs, below are frequently used commands which will be needed if while inserting, updating, deleting, view etc To see exiting full job details: $ autorep -J jobname -q. If you want to see all job inside box, its same command as you see any job details only here you will have to specify box job. Well guys, the previous post about AutoSys was more like a cheat-sheet to AutoSys commands. But now in this post I will discuss more detailed about AutoSys. AutoSys is an automated job control system for scheduling, monitoring, and reporting purpose. These jobs can reside on any AutoSys-configured machine that is attached to.
AutoSys System components1. Event server (AutoSys database)
2. Event processor
3. Remote agent
Event Server
The event server is a AutoSys database which stores all system information and events as well as all job, monitor, and report definitions. Sometimes this database is also called as a data server, which actually describes a server instance. That is, it is either a UNIX or Windows process, and it is associated data space (or raw disk storage), that can include multiple databases or tablespaces.
Event Processor
This is main component of the autosys system. This processes all the events it reads from dataserver. The event processor is the program, running either as a UNIX process or as a Windows service that actually runs AutoSys. It schedules and starts jobs. When you start the event processor it continually scans the database for events to be processed. When it finds one, it checks whether the event satisfies the starting conditions for any job in the database.
Remote Agent

On a UNIX machine, the remote agent is a temporary process started by the event processor to perform a specific task on a remote (client) machine. On a Windows machine, the remote agent is a Windows service running on a remote (client) machine that is directed by the event processor to perform specific tasks.
The remote agent starts the command specified for a given job, sends running and completion information about a task to the event server, then exits. If the remote agent is unable to transfer the information, it waits and tries again until it can successfully communicate with the database.
Basic functionality of AutoSys
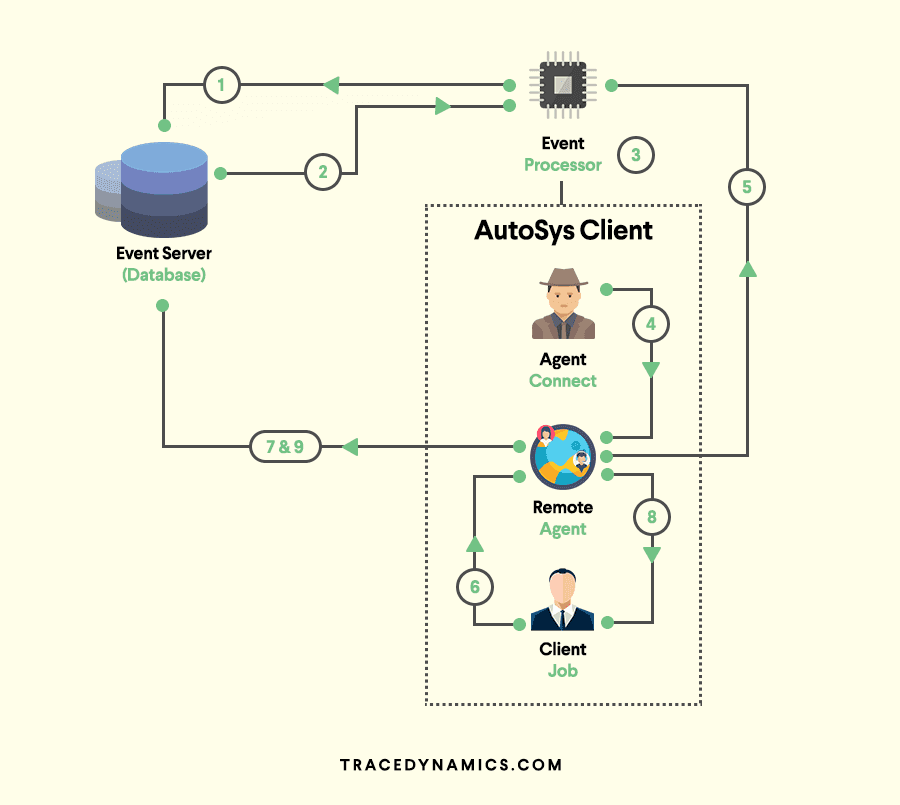
Below is the diagram which explains the basic functionality, please check the explanation.
Explanation
1. The event processor scans the event server for the next event to process. If no event is ready, the event processor scans again in five seconds.

2. The event processor reads from the event server that an event is ready. If the event is a STARTJOB event, the job definition and attributes are retrieved from the Event Server, including the command and the pointer (full path name on the client machine) to the profile file to be used for the job. In addition, for jobs running on Windows machines, the event processor retrieves from the database the user IDs and passwords required to run the job on the client machine.
3. The event processor processes the event. If the event is a STARTJOB, the event processor attempts to establish a connection with the remote agent on the client machine, and passes the job attributes to the client machine.
The event processor sends a CHANGE_STATUS event marking in the event server that the job is in STARTING state.
4. On a UNIX machine, the inetd invokes the remote agent. On a Windows machine, the remote agent logs onto the machine as the user defined as the job’s owner, using the user IDs and passwords passed to it from the event processor.
5. The remote agent sends an acknowledgment back to the event processor indicating that it has received the job parameters. The socket connection is terminated. At this point, the event processor resumes scanning the event server database, looking for events to process.
6. The remote agent starts a process and executes the command in the job definition.
7. The remote agent issues a CHANGE_STATUS event marking in the event server that the job is in RUNNING state.
8. The client job process runs to completion, then returns an exit code to the remote agent and quits
Defining autosys job
 There are various parameters to define autosys job. Starting from profile, timezone, start time, starting condition and so on. There are the two methods you can use to create job definitions:
There are various parameters to define autosys job. Starting from profile, timezone, start time, starting condition and so on. There are the two methods you can use to create job definitions:1. Using the AutoSys Graphical User Interface (GUI).
2. Using the AutoSys Job Information Language (JIL) through a command-line interface.
In this tutorial we will use JIL language to create autosys jobs.
JIL stands for Job Information Language. Using this you can instruct autosys to save job definitions. This information saved in autosys database. You can also create a jil file which contains job definition. You can then pass this jil file to autosys.
Essential attributes for defining job
1. Job Name
JIL Keyword : insert_job. Name used to identify the job.
2. Job Type
a. JIL Keyword : job_type. The job type is one of job types: command (c), file watcher (f) or box (b).
3. Owner
 a. JIL Keyword : owner
a. JIL Keyword : ownerThe job owner specifies whose user ID the command will be run under on the client machine. This attribute is automatically set to the user who invoked jil or the GUI to define the job, and cannot be changed except by the edit superuser.
Other job attributes:
1. command: The command attribute can be the name of any command, executable, UNIX shell script or batch file, and its arguments.
2. machine: This attribute specifies the client machine on which the command should be run.
3. date_condition: The start date/time dependencies attribute is a toggle, which specifies whether or not there are date, time, or both, conditions required for starting the job.
4. days_of_week: The days of the week attribute specifies the days on which the job should be run.
Sample jil file for command job echoJob.jil
--------------------------------------------
1 insert_job:echoJob
2 machine:unixMachine
3 owner:username
4 command:echo “Hello this is command job”
--------------------------------------------
To add this job in atosys db. Run following command from unix:
jil < echoJob.jil
This command will add “echoJob” job to autosys databse
Commands to control the job
Start job command
--------------------------------------------
sendevent –E FORCE_STARTJOB -J
sendevent -E STARTJOB -J
--------------------------------------------
To put jobs on OFF ICE or ON ICE
--------------------------------------------
sendevent -E OFF_ICE -J
sendevent -E ON_ICE -J
sendevent -E KILLJOB –J 'Job Name Here'
--------------------------------------------
Meaning of AutoSys status
-----------------------------------------
Curtesy:
AutoSys System components1. Event server (AutoSys database)
2. Event processor
3. Remote agent
Event Server
The event server is a AutoSys database which stores all system information and events as well as all job, monitor, and report definitions. Sometimes this database is also called as a data server, which actually describes a server instance. That is, it is either a UNIX or Windows process, and it is associated data space (or raw disk storage), that can include multiple databases or tablespaces.
Event Processor
This is main component of the autosys system. This processes all the events it reads from dataserver. The event processor is the program, running either as a UNIX process or as a Windows service that actually runs AutoSys. It schedules and starts jobs. When you start the event processor it continually scans the database for events to be processed. When it finds one, it checks whether the event satisfies the starting conditions for any job in the database.
Remote Agent
On a UNIX machine, the remote agent is a temporary process started by the event processor to perform a specific task on a remote (client) machine. On a Windows machine, the remote agent is a Windows service running on a remote (client) machine that is directed by the event processor to perform specific tasks.
The remote agent starts the command specified for a given job, sends running and completion information about a task to the event server, then exits. If the remote agent is unable to transfer the information, it waits and tries again until it can successfully communicate with the database.
Basic functionality of AutoSys
Below is the diagram which explains the basic functionality, please check the explanation.
Explanation
1. The event processor scans the event server for the next event to process. If no event is ready, the event processor scans again in five seconds.
2. The event processor reads from the event server that an event is ready. If the event is a STARTJOB event, the job definition and attributes are retrieved from the Event Server, including the command and the pointer (full path name on the client machine) to the profile file to be used for the job. In addition, for jobs running on Windows machines, the event processor retrieves from the database the user IDs and passwords required to run the job on the client machine.
3. The event processor processes the event. If the event is a STARTJOB, the event processor attempts to establish a connection with the remote agent on the client machine, and passes the job attributes to the client machine.
The event processor sends a CHANGE_STATUS event marking in the event server that the job is in STARTING state.
4. On a UNIX machine, the inetd invokes the remote agent. On a Windows machine, the remote agent logs onto the machine as the user defined as the job’s owner, using the user IDs and passwords passed to it from the event processor.
5. The remote agent sends an acknowledgment back to the event processor indicating that it has received the job parameters. The socket connection is terminated. At this point, the event processor resumes scanning the event server database, looking for events to process.
6. The remote agent starts a process and executes the command in the job definition.
7. The remote agent issues a CHANGE_STATUS event marking in the event server that the job is in RUNNING state.
8. The client job process runs to completion, then returns an exit code to the remote agent and quits
Defining autosys job
There are various parameters to define autosys job. Starting from profile, timezone, start time, starting condition and so on. There are the two methods you can use to create job definitions:
1. Using the AutoSys Graphical User Interface (GUI).
2. Using the AutoSys Job Information Language (JIL) through a command-line interface.
In this tutorial we will use JIL language to create autosys jobs.
JIL stands for Job Information Language. Using this you can instruct autosys to save job definitions. This information saved in autosys database. You can also create a jil file which contains job definition. You can then pass this jil file to autosys.
Essential attributes for defining job
1. Job Name
JIL Keyword : insert_job. Name used to identify the job.
2. Job Type
a. JIL Keyword : job_type. The job type is one of job types: command (c), file watcher (f) or box (b).
3. Owner
a. JIL Keyword : owner
The job owner specifies whose user ID the command will be run under on the client machine. This attribute is automatically set to the user who invoked jil or the GUI to define the job, and cannot be changed except by the edit superuser.
Other job attributes:
1. command: The command attribute can be the name of any command, executable, UNIX shell script or batch file, and its arguments.
2. machine: This attribute specifies the client machine on which the command should be run.
3. date_condition: The start date/time dependencies attribute is a toggle, which specifies whether or not there are date, time, or both, conditions required for starting the job.
4. days_of_week: The days of the week attribute specifies the days on which the job should be run.
Sample jil file for command job echoJob.jil
--------------------------------------------
1 insert_job:echoJob
2 machine:unixMachine
3 owner:username
Autosys Cheat Sheet
4 command:echo “Hello this is command job”
 --------------------------------------------
--------------------------------------------To add this job in atosys db. Run following command from unix:
jil < echoJob.jil
This command will add “echoJob” job to autosys databse
Commands to control the job
Start job command
--------------------------------------------
Autosys Commands Cheat Sheet
sendevent –E FORCE_STARTJOB -JAutosys Jil Command Reference
sendevent -E STARTJOB -J
--------------------------------------------
To put jobs on OFF ICE or ON ICE
--------------------------------------------
sendevent -E OFF_ICE -J
sendevent -E ON_ICE -J
sendevent -E KILLJOB –J 'Job Name Here'
--------------------------------------------
Meaning of AutoSys status
-----------------------------------------
Curtesy:
