An element's atomic number tells us the number of what?
- The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom determines an element's atomic number. In other words, each element has a unique number that identifies how many protons are in one atom of that element. For example, all hydrogen atoms, and only hydrogen atoms, contain one proton and have an atomic number of 1.
- The Crossword Solver found 20 answers to the neon's atomic number crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to American-style crosswords, British-style crosswords, general knowledge crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the answer length or the answer pattern to get better results.
1 Answer
Atomic Number Name Symbol Group Period Number Block State at. STP Occurrence Description 1 Hydrogen H 1 1 s Gas Primordials Non-metal 2 Helium He 18 1 s Gas Primordial Noble gas 3 Lithium Li 1 2 s Solid Primordial Alkali metal 4 Beryllium Be 2 2 s Solid Primordial Alkaline earth metal 5 Boron B 13 2 p Solid Primordial Metalloid 6 Carbon C 14 2 p.
Explanation:
Mac os transfer for android. So if
And if
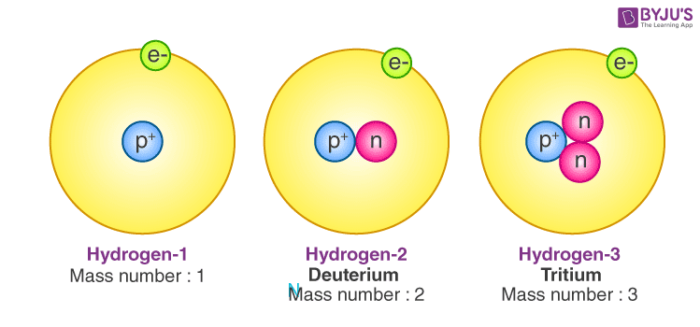
And if

..............
And if
Free app uninstaller for mac.
And the next concept to grasp is that of
If
The atomic mass printed on the Periodic Table is the weighted average of the isotopes. And as
Atomic Structure Answer Key
Related questions
