Normal oxygen saturation is usually between 96% and 98%. Any level below this is considered dangerous and warrants urgent oxygen supplementation and/or treatment for your lung condition. Verywell / Laura Porter How Blood Becomes Oxygenated.
- Normal Oxygen Level In Blood
- Normal Oxygen Saturation Levels
- Normal Oxygen Saturations
- Normal Oxygen Saturation By Age
- Normal Oxygen Range
Oxygen levels and Covid-19
- 7 hours ago 'The oxygen pressure remained below normal for the last three days. This is the first time in this period that normal pressure has been achieved,' an official said.
- Normal Oxygen Level in Blood For most people, an oxygen level of 95-100% is considered to be normal. When the level of oxygen is within this range, it is considered to be optimum for smooth functioning of the cells. A level that is below 95% is a cause for concern and warrants an examination or testing by a medical personnel.
- 6 hours ago 'The oxygen pressure remained below normal for the last three days. This is the first time in this period that normal pressure has been achieved,' an official said. The hospital received 3 MT of oxygen around 6 pm, which will last up to midnight. 'The hospital did not have to press the panic button the whole day. No SOS calls were made.
- 7 hours ago 'The oxygen pressure remained below normal for the last three days. This is the first time in this period that normal pressure has been achieved,' an official said. The hospital received 3 MT of oxygen around 6 pm, which will last up to midnight. 'The hospital did not have to press the panic button the whole day. No SOS calls were made.
Vital signs, those fluorescent green numbers that beep, ding, and dash across black screens on the monitors in hospital rooms, have become a new source of angst during the coronavirus pandemic.
One of those vital signs is blood oxygen level, and in the hospital, it's measured with a pulse oximeter. These devices are attached to your finger and use a beam of light to measure oxygen in the blood.
Patients with Covid-19 can sometimes have relatively mild symptoms and seem to be perfectly oxygenated, even while their blood oxygen levels are perilously low. As a result, they may need an emergency supply of supplemental oxygen.

Covid-19 patients healthy enough to be discharged are often sent home with instructions to self-monitor, which has triggered a demand for pulse oximeters you can buy and use at home.
The tiny devices, which range in price from $20 to $200, clamp snugly over the index finger and display the percentage of oxygen being carried around by your blood. But how accurate are they? And how do you read them?
Three doctors, all of whom were on the coronavirus frontlines during the first peak in hard-hit New York City, warn that the results and efficacy can differ from unit to unit.
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) considers pulse oximeters to be prescription medical devices, but most of those sold on the internet or in drugstores are labeled 'not for medical use' and have not been reviewed for accuracy. Still, having a pulse oximeter on hand may come in handy, as long as users exert common sense.
Consumers should use the devices while under a physician's care and follow up if blood oxygen readings seem to dip precipitously, especially when paired with symptoms like shortness of breath, cough, and fever.
Here's what you need to know about checking oxygen levels with a pulse oximeter at home.
© Kayoko Hayashi/Getty ImagesUnderstanding normal oxygen levels
The average person takes about 20,000 breaths a day. Keeping normal oxygen levels is a finely-tuned science.
'We've got to get oxygen from the atmosphere into our lungs; we've got to get the oxygen from our lungs into our bloodstream, and then we've got to get the blood to our cells, and our cells have to take out that oxygen. So, all those things have to work right for things to go well,' explains Amit Uppal, MD, director of critical care at Bellevue Hospital in New York City.
To date, Dr. Uppal says he's overseen the treatment of more than 300 Covid-19 patients, all with varying levels of blood oxygen.
What is a good oxygen level?
'Normal people who have working lungs, and all those steps are going well, their blood oxygen level will usually be 96-100 percent,' adds Dr. Uppal.
Normal Oxygen Level In Blood
A few notches down at 94 percent, he says, will be considered 'abnormal,' but that won't necessarily be cause for alarm. 'For the vast majority of people, nothing bad will happen. Nobody's going to have a cardiac arrest with a blood oxygen level in that [94] range.'
If someone has heart or lung disease, says Dr. Uppal, those 'normal' numbers may be a bit lower. There is, however, a universal threshold that signifies a dangerous situation.
'I think anything below 90 we definitely get very concerned. When it gets down into the 80 percent range or less than 80 percent range is when really bad things can happen.'
There is a possibility an individual's oxygen levels can be too high. However, this often occurs in people who are on supplemental oxygen.
High levels can be measured via an arterial blood gas (ABG) test, which is accurate, but invasive. This is a blood test that requires blood to be drawn from the artery, which is usually done in the wrist.
This measures your blood oxygen level and can also detect other gas levels in the blood, as well as your pH, or how acidic your blood is.
What happens when blood oxygen dips too low
When your blood oxygen reading falls below that 90 percent threshold, you'll likely feel a variety of symptoms.

'It includes feeling short of breath, and increased respiratory rate. So, if you're at rest and noticing that you're having to work hard to breathe, that's a sign,' says Reed Caldwell, MD, chief of service at NYU Langone's Cobble Hill emergency department.
You could also experience cyanosis, meaning you could turn blue or gray due to the blood's poor oxygenation, or you might have confusion, adds Dr. Caldwell.
'Your brain thrives on oxygen,' says Dr. Caldwell. 'So, people can be confused—or even unconscious.'
Normal Oxygen Saturation Levels
One of the more concerning Covid-19 symptoms
Infectious disease epidemiologist Syra Madad studied and led response teams during some of this generation's most serious health crises including Ebola, Zika, and measles. But she says nothing frightens her more than Covid-19.
'From my standpoint, and all the different epidemics I've responded to, this has been something I have never seen before,' says Madad, who is the senior director of the system-wide special pathogens program at New York City Health + Hospitals.
Last fall, she asked Congress not to let a pandemic-protection bill lapse and is now dealing with the fallout as the U.S. currently has 500,000-plus deaths from Covid-19 and counting. (It's documented in a new Netflix documentary, Pandemic: How to Prevent an Outbreak, featuring Madad.)
'Some people will be perfectly fine and have no issues,' says Madad. 'And other people will come in with their oxygen saturation levels below 94, 93, 92 percent, or even lower than that. And they look perfectly fine. It's one of those silent hypoxic killers almost.'
What is hypoxemia?
When someone is hypoxic, they're experiencing hypoxia or the absence of enough oxygen inside the body's tissues to sustain bodily functions. (A similar term, hypoxemia, means low oxygen levels in the blood, rather than the body's tissues.)
Normal Oxygen Saturations
Covid-19 patients with this sign have been dubbed as having 'happy hypoxia.'
Instead of gasping for air, they're texting on their smartphones. 'They're not showing the signs and symptoms like bluish lips, trouble breathing, anything like that,' says Madad. 'So you have no idea they're experiencing this symptom, and then you check their blood oxygen levels, and you realize they're at very alarmingly low levels.'
In a June article in the Journal of Medical Systems, author Jason Teo further explained how silent hypoxia sneaks up on people.
Normal Oxygen Saturation By Age
'The air sacs in Covid-19 patients' lungs do not fill with fluid or pus as in normal pneumonia infections but rather the virus only causes the air sacs to collapse, thereby reducing the oxygen levels that lead to hypoxia in these patients but still maintains the lungs' normal ability to expel carbon dioxide,' wrote Teo.
He proposes that smartphone-based oximeters may one day unlock the key to more widespread early detection.
How to check blood oxygen using a pulse oximeter
Although they were scarce early in the pandemic, pulse oximeters are now easy to find. (An Amazon search returns 1,000 results.) Many are battery-powered and simply need to be turned on and placed on your index finger.
Pulse oximeters display two readings—one is SpO2, which is the oxygen saturation level in your blood, and your pulse rate.
'Monitoring [with an oximeter] is OK as long as you're under the guidance of a medical physician,' says Dr. Caldwell. 'I think it could be a potentially disastrous situation to be in if people take it upon themselves to just look up the numbers on the internet and then monitor their oxygen.'
Also, warns Dr. Uppal: 'I don't think that the general public of people who have no symptoms and have not tested positive for Covid-19 need to be checking their pulse oxygen 10 times a day.'
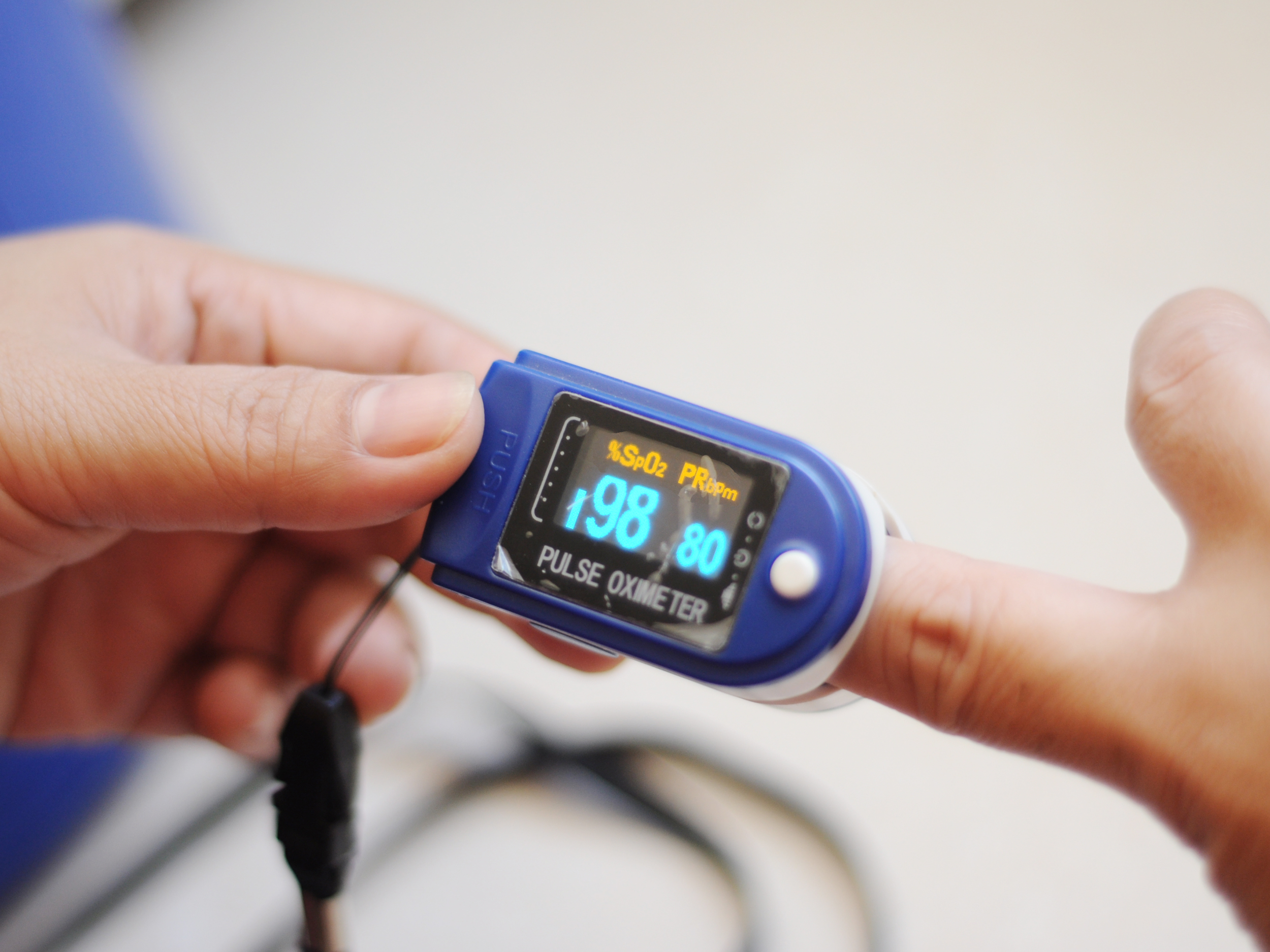
When to call a doctor
Early intervention could improve health outcomes for patients presenting with lowered blood oxygen. People with low oxygen levels will often require supplemental oxygen to increase their oxygen saturation.
'We know that some people are still kind of avoidant of health care because they are afraid to get Covid-19,' says Dr. Caldwell. 'And if you can't breathe, you need to be seen. And if your oxygen level is low, you need to be evaluated because your chances of a bad outcome trying to manage [while] stuck at home, it still needs to outweigh your chance of your family picking up something in a health care setting.'
Or, someone could have something other than Covid-19 altogether. 'A blood clot in your lung can give you low oxygen' notes Dr. Caldwell, 'that's something that would need prompt attention.'
Now, doctors may also suggest home supplemental oxygen, which is prescribed. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for using home supplemental oxygen to prevent any serious complications.
Preventing Covid-19
Dr. Uppal says he has had the fortune of helping some of his Covid-19-patients recover and the misfortune of saying goodbye to others. This includes longtime colleagues for whom he fought hard for.
A particularly heart-wrenching case, he remembers, was a mother and father who passed away due to Covid-19, orphaning their two young children.
Today, nearly an entire year into the pandemic, Dr. Uppal says there are far more tools in physicians' toolbox to fight back against respiratory diseases like Covid-19.
'Steroids seem to help patients who start to deteriorate. It seems to reduce the likelihood that they end up on a breathing machine or reduce the likelihood that they end up in the ICU,' Dr. Uppal says. 'Remdesivir seems to help reduce the severity in patients. And some data just came out that a drug called tocilizumab also is beneficial.'
But nothing used to treat Covid-19 is as useful as taking measures to prevent it.
'I think what I'd like to emphasize is that getting better at treating the disease once people have it doesn't make it go away.' Dr. Uppal adds, 'The thing that we're still going to have to lean on is preventing it from spreading in the first place.'
The post What Is a Normal Oxygen Level and How Can I Check Mine? appeared first on The Healthy.
- What are vital signs?
- What is a normal oximeter reading?
Vital signs are measurements of the body’s basic functions. Normal vital signs change with age, sex, weight, exercise tolerance, and overall health. The four main vital signs that are usually monitored include:
- Body temperature
- Pulse rate (heart rate)
- Rate of breathing (respiration rate)
- Blood pressure
Contents
Pulse oximeter readings chart
Often called the “fifth” vital sign, pulse oximetry is a non-invasive way to monitor oxygen saturations. Prior to the use of pulse oximeters, the amount of oxygen in the blood could only be measured by drawing blood directly from an artery and analyzing that.
Pulse oximetry is generally done by using a device placed on the end of a finger or on the earlobe. Light of two wavelengths passes through the tissue and the oxygen saturation is measured. The measurement is the percent saturation of oxygen which is being carried by hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is the oxygen carrying pigment in our red blood cells.
A normal reading is 95% to 99%. Readings below 90% often indicate that someone needs to have supplemental oxygen.
Pulse oximeter oxygen saturation
Pulse oximetry allows a rapid noninvasive estimate of arterial oxygen saturation. Since its development in the 1970s, it has made a significant impact, particularly in the fields intensive care medicine.
Most modern pulse oximeters determine arterial hemoglobin saturation through the use of two lightemitting diodes in the red (660 nm) and infrared (940 nm) spectrum.
The differential absorption of these two wavelengths of light by oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin during pulsatile blood flow allows for accurate estimation of arterial oxygen saturation under most conditions.
However, pulse oximeters can give erroneous from a variety of causes, including hypoperfusion, nail polish, darker skin pigmentation, venous pulsations, and, perhaps most frequently, motion artifact.
Medical Grade Pulse oximeter
Clinicians must consider these possible causes of error when interpreting pulse oximetry results, especially those that are not consistent with a patient’s clinical status and medical history.
Clinically significant desaturations in an ambulatory setting are uncommon in patients without significant pathologic pulmonary conditions or pulmonary vascular disease.
The potential of erroneous readings must be considered, especially measurements made during exercise.
Pulse oximeter 6 minute walk test
Continuous pulse oximetry is commonly combined with a 6-min walk test (6MWT) in the ambulatory setting when evaluating dyspnea.
Prior American Thoracic Society guidelines for the 6MWT recommend against continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation during a 6MWT3 because of concerns about erroneous readings.
Normal Oxygen Range
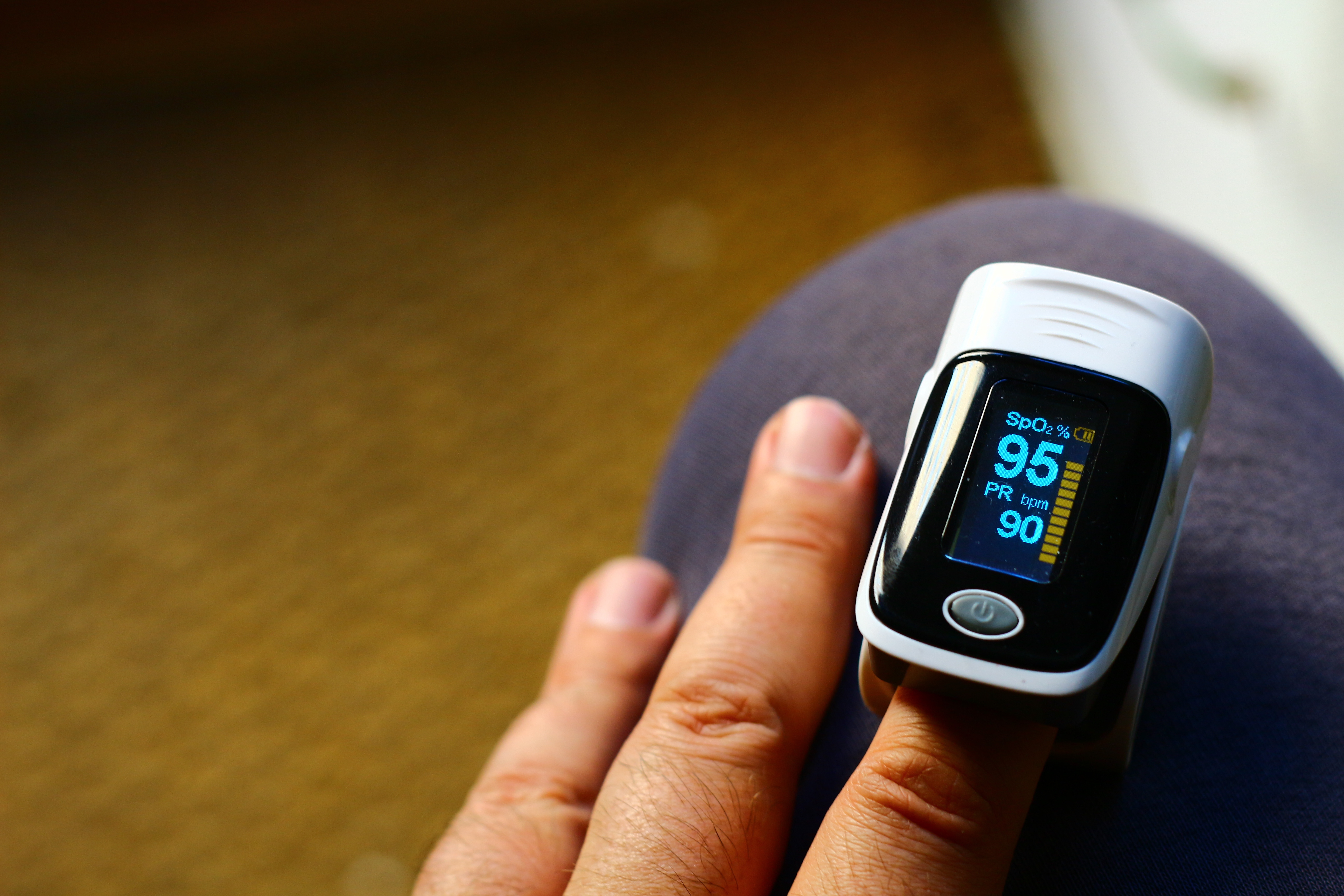

Prior studies have shown significant inaccuracies in this setting, likely due to motion artifact.
In addition, many handheld pulse oximeters available in the office setting do not display oximetry waveforms or alternative evaluations of measurement quality.
This leads to a greater risk of misinterpretation, as a digital readout is assumed to be accurate without a proper understanding of how that measurement is made.
6-minute walk test normal values
However, more recent European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society guidelines for field walking tests (including 6MWT) support the use of continuous oximetry because of evidence showing that the lowest saturation does not necessarily occur at the end of the test.
Patients suspected of having desaturations by pulse oximetry during a 6MWT are regularly referred to our facility for formal cardiopulmonary exercise testing.
These evaluations are a source of significant expense, including that of the cardiopulmonary exercise testing itself, as well as risk to the patient from invasive procedures or radiation exposure that may be unnecessary if their pulse oximetry testing results were inaccurate.
Pulse oximeter uses and limitations
Applications for use:
Pulse oximetry is used extensively in medical offices and hospitals. It is also now widely used in the home setting to monitor people with heart and lung problems. Uses include:
- Monitoring the level of supplemental oxygen needed for someone with COPD, CHF,or other diseases.
- Monitoring someone who is ill with a respiratory infection.
- A fall in oxygen can be a warning that the person needs further evaluation immediately.
- Monitoring oxygen levels during sleep can help diagnose sleep apnea.
Pulse oximeter false readings
There are some limitations of this technology and can result in either falsely low or high oxygen saturation readings:
- Low blood pressure as blood does not circulate well into the hands.
- Hypothermia (very low body temperature) as blood vessels will constrict or narrow.
- Motion such as shivering or seizures can affect readings.
- Congenital medical conditions of abnormal hemoglobin or severe anemia canaffect readings.
- Poor sugar control in diabetics has been associated with high oxygen saturation readings due to an increase in oxygen “sticking” to hemoglobin in the blood.
- Nail polish or artificial nails could affect the reading but the probe can be placed sideways on the finger so that the pulsed light does not go through the nails. Dark skin pigmentation can also affect readings.
- Intense daylight, fluorescent light and other intense light can cause falsely lowreadings.
Pulse Oximeter made in USA
- Ever wonder if there are pulse oximeters made in the USA?
- How many medical device manufacturers are there in the United States?
FDA approved pulse oximeter

Pulse oximetry is a test used to measure the oxygen level (oxygen saturation) of the blood. It is an easy, painless measure of how well oxygen is being sent to parts of your body furthest from your heart, such as the arms and legs.
Fingertip Pulse Oximeters
- What is the best pulse oximeter?
- What is a normal oxygen saturation level?
- Are any oximeters made in the USA?
- Pulse oximeters FDA approved and more…
Pulse Oximeters: Answering Your Frequently Asked Questions
